







- Stock: Out Of Stock
- Model: EX.RK09D1130C1B
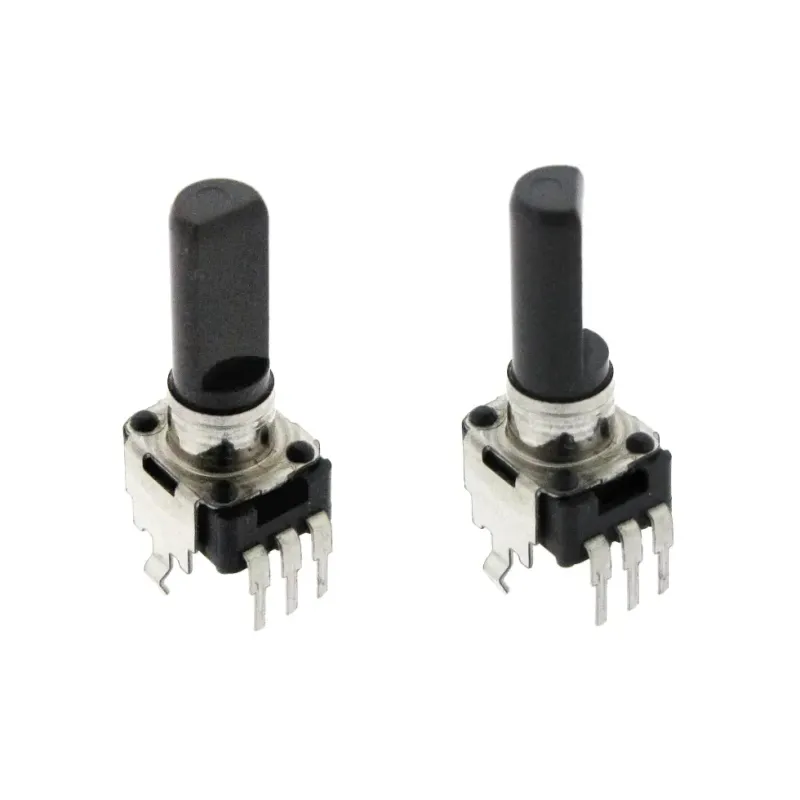
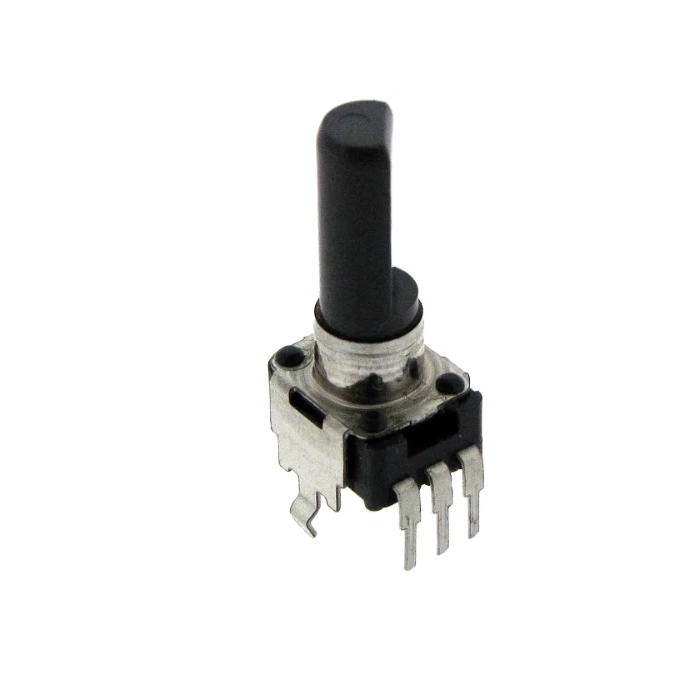
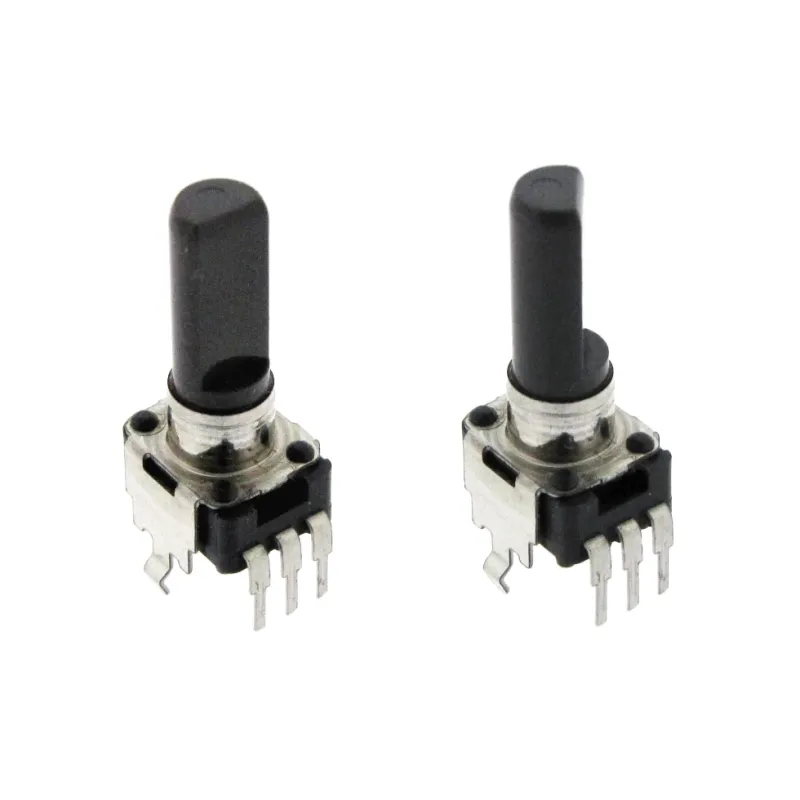
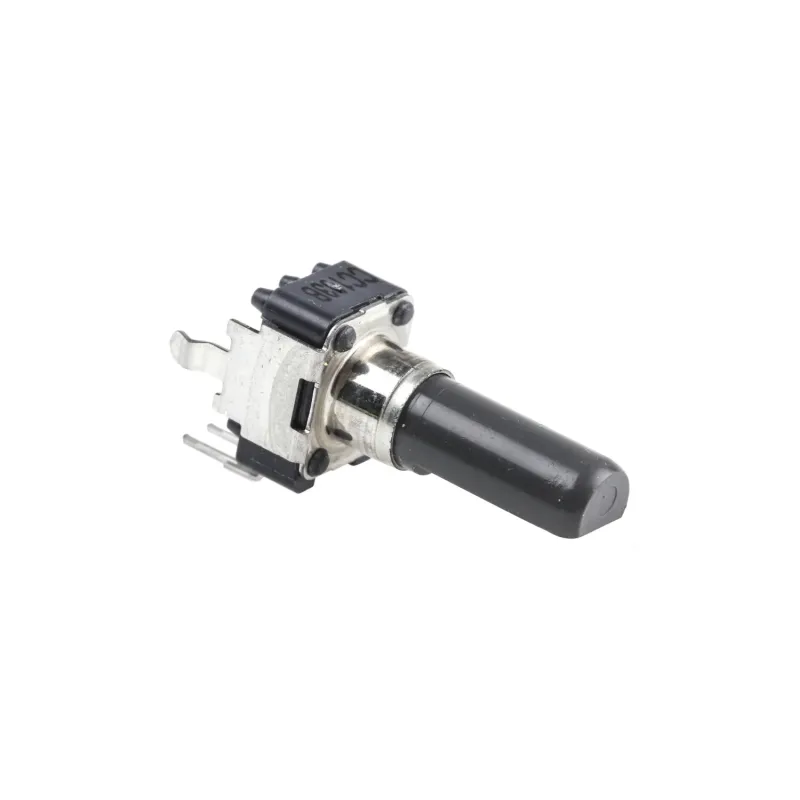
Alps Alpine RK09D1130C1B 10K Potentiometer Original Japan
9 mm insulated plastic shaft snap-in rotary potentiometer — Alps / Alps Alpine. Compact, single-turn control ideal for PCB and front-panel adjustments in low-power electronics, Arduino projects, Raspberry Pi builds (with external ADC), and embedded microcontroller designs.
🧭 Overview
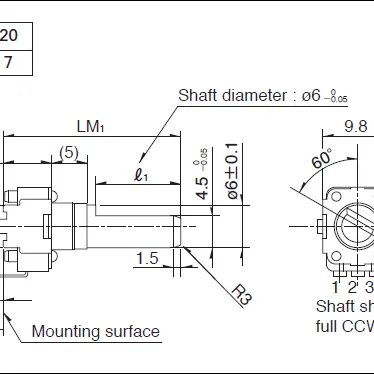
The RK09D1130C1B is a space-saving, 9 mm rotary potentiometer with a linear (1B) taper and snap-in panel mounting. Its flat insulated shaft and PCB solder pins streamline integration into compact enclosures and densely populated boards. Designed for low-power adjustment tasks, it provides smooth, predictable control for DC circuits, user interfaces, and modular electronics.
⭐ Features & Benefits
- 🧩 Compact 9 mm body saves valuable PCB area in tight layouts and small enclosures.
- 🔩 Snap-in panel mounting simplifies secure front-panel installation and alignment.
- 🎚️ Linear taper (1B) delivers smooth, predictable adjustment—ideal for DC control and calibration.
- 🛡️ High insulation resistance and robust dielectric strength support low-voltage safety requirements.
- 🔄 Single-turn operation with moderate durability (5,000 cycles) for infrequent adjustment duties.
📊 Electrical & Mechanical Specifications
- Total resistance: 10 kΩ ±20%
- Taper (curve): Linear (1B)
- Power rating: 0.05 W (1/20 W)
- Maximum operating voltage: 50 V AC / 20 V DC
- Insulation resistance: ≥ 100 MΩ @ 250 V DC
- Dielectric strength (voltage proof): 250 V AC, 1 minute
- Mechanical rotation angle: 300° ±5°
- Operating torque: 1 – 8 mN·m
- Lifespan: 5,000 cycles
- Operating temperature: −10 °C to +70 °C
- Shaft: Flat, insulated (plastic), approx. 20 mm length
- Mounting: Snap-in panel + PCB solder pins
- Tolerance: ±20%
- Form factor: 9 mm body, single-turn rotary
⚠️ Warnings & Application Notes
- Low-power device: 0.05 W rating—do not use in high-current or high-power applications.
- Tolerance: ±20% may be unsuitable where precise resistance values are critical without calibration.
- Soldering: Avoid excessive heat. Tip ≈ 350 °C, exposure ≤ 3 s recommended.
- Load impedance: Contact resistance can impact low-impedance loads. Use a load much higher than the potentiometer value (rule of thumb: ≫ 10 kΩ).
- Environment: Avoid condensation, high humidity, and liquids to maintain insulation performance.
- Mechanical support: Longer exposed shafts can be sensitive to vibration—add support if necessary.
🔧 Typical Applications
- Front-panel level/volume controls and user-interface knobs
- Small consumer electronics and handheld instruments
- Prototype boards and calibration trimmers in lab setups
- Low-power tuning in Arduino and Raspberry Pi-based projects (with ADC)
- Voltage divider for analog control inputs in microcontroller modules
🧠 Integration Tips (Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Microcontrollers)
- Use as a voltage divider between your reference (e.g., 5 V or 3.3 V) and ground; read the wiper with an ADC.
- Arduino: Connect the wiper to an analog input (A0–A5). Ensure the load impedance from the wiper is high to minimize error.
- Raspberry Pi: Requires an external ADC module (e.g., MCP3008) to read the analog voltage.
- Keep the wiper trace short and away from noisy digital lines to reduce interference.
- Stay within the specified maximum operating voltage and power rating to avoid damage.
Looking for a printable datasheet layout, a ready-to-list product page, or a variant/alternatives comparison? Tell us your preferred format and we’ll prepare it. ✅






